

| Color | Lab grown Padparadscha |
| Size | 10*8 mm |
| Shape | Oval CAB |
| Color | Pink |
| Clarity | vvs |
| Mohs Scale | 9 |
| Reflective Index | 1.76-1.77 |
| Density | 3.99-4.02 g/cm3 |
| Temperature resistance (highest limit) | 1200°C |
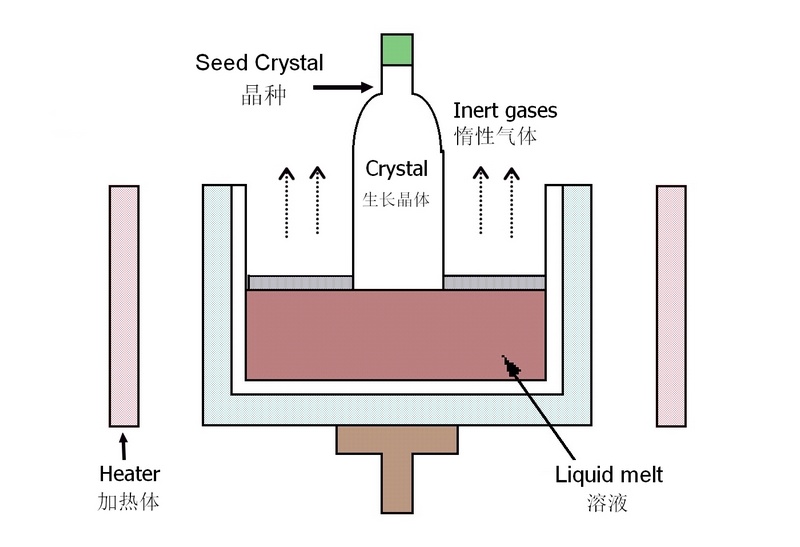
“提拉法”指的是柴拉夫斯基法(Czochralski method),这是一种从熔体中提拉生长单晶宝石的核心技术。
这种方法与工业上用于生长半导体硅单晶的技术同源,其核心原理是:
1.原料熔化:将宝石的原料(如氧化铝Al₂O₃和致色剂)放入耐高温的坩埚(如铱、钼或石墨坩埚)中,通过高频线圈或电阻加热至
极高温度(例如,合成红宝石需加热至2050℃以上)使其完全熔化。
2.接触与结晶:将一颗微小的、定向的天然或人造宝石籽晶,缓慢下降并接触熔体表面。
3.提拉与旋转:在严格控制的条件下,籽晶被缓慢地向上提拉并同时旋转。熔体在籽晶与熔体的交界面上,按照籽晶的晶体结构不断
冷却、结晶,从而生长出与籽晶取向一致的单晶宝石。
4.工艺控制:整个过程需要精确控制温度梯度、提拉速率(通常为每小时6-15毫米)和旋转速度,以确保晶体生长的均匀性和质量。
工艺中常采用“缩颈-扩肩-等径-收尾”等步骤来优化晶体结构。
这种方法生长的宝石晶体光学均一性高、位错密度低,且能生长出大尺寸的单晶,是目前高品质培育宝石(尤其是刚玉类)最主要
的生产方法之一。
Czochralski method is a core technology for growing single-crystal gemstones from a melt.
This method is homologous with the technology used industrially to grow semiconductor silicon single crystals. Its core principle is
as follows:
1.Raw Material Melting: The gemstone's raw materials (e.g., aluminum oxide Al₂O₃ and dopants) are placed into a
high-temperature-resistant crucible (e.g., iridium, molybdenum, or graphite crucibles) and heated to extremely high
temperatures (e.g., synthetic ruby requires heating above 2050℃) using induction coils or resistive heating until completely melted.
2.Contact and Crystallization: A small, oriented natural or synthetic gemstone seed crystal is slowly lowered and brought into
contact with the melt surface.
3.Pulling and Rotation: Under strictly controlled conditions, the seed crystal is slowly pulled upward while simultaneously rotating.
The melt at the interface between the seed crystal and the melt continuously cools and crystallizes according to the crystal structure
of the seed, thereby growing a single crystal gemstone with the same orientation as the seed.
4.Process Control: The entire process requires precise control of temperature gradient, pulling rate (typically 6-15 millimeters per
hour), and rotation speed to ensure uniformity and quality of crystal growth.
Common steps in the process include "necking, shoulder expansion, diameter control, and tailing" to optimize the crystal structure.
Gemstone crystals grown by this method exhibit high optical homogeneity, low dislocation density, and can be grown to large sizes.
It is one of the primary production methods for high-quality synthetic gemstones, especially corundum family gems.
Copyright 2016 Changjiang Gems, Cubic Zirconia Ltd. All Rights Reserved. ICP88888888 Powered by 17uhui




















